Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just a buzzword in the tech industry; it has become an essential force reshaping every aspect of our lives. Education, one of the most vital pillars of society, is undergoing a profound transformation driven by AI-powered technologies. From personalized learning experiences to automated administrative tasks, AI in education is enabling smarter classrooms, empowered teachers, and more engaged students.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how AI is revolutionizing education, its benefits and challenges, and what the future holds for AI-driven learning environments.
Understanding AI in Education
AI in education refers to the use of artificial intelligence technologies—such as machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision—to enhance teaching, learning, and administrative processes. This includes:
Personalized learning systems that adapt to student needs.
Intelligent tutoring systems that provide feedback in real-time.
Automation of repetitive tasks like grading and attendance.
Data-driven insights for educators and administrators.
The goal is not to replace teachers but to empower them and students with tools that make education more effective, inclusive, and accessible.
How AI Is Transforming Classrooms
a) Personalized Learning at Scale
One of the most significant impacts of AI in education is the ability to deliver personalized learning experiences. Traditional classrooms often struggle to accommodate different learning speeds, styles, and abilities.
AI-powered adaptive learning platforms such as DreamBox, Carnegie Learning, and Khan Academy’s AI-driven tools analyze each student’s performance, identify gaps, and deliver tailored content. This individualized approach helps students grasp concepts faster and retain knowledge longer.
Example: An AI system can detect that a student is struggling with fractions and automatically provide extra practice problems, videos, or even recommend peer study sessions.
b) Intelligent Tutoring Systems
AI-based tutoring systems simulate one-on-one tutoring. They offer explanations, hints, and feedback in real-time, much like a human tutor. These systems are available 24/7, giving students the flexibility to learn at their own pace.
Such systems can support subjects ranging from math to language learning. For example, Duolingo uses AI to personalize language lessons for each learner, while tools like Squirrel AI in China provide AI-driven tutoring for K–12 students.
c) Automation of Administrative Tasks
Teachers spend a large portion of their time grading papers, taking attendance, and handling administrative paperwork. AI can automate these repetitive tasks, freeing educators to focus on teaching and mentoring.
Automated Grading: AI tools can grade multiple-choice tests instantly and are increasingly capable of evaluating essays using NLP algorithms.
Attendance Systems: AI-driven facial recognition can take attendance automatically in classrooms.
Scheduling and Resource Allocation: AI can optimize timetables and classroom resources to reduce administrative overhead.
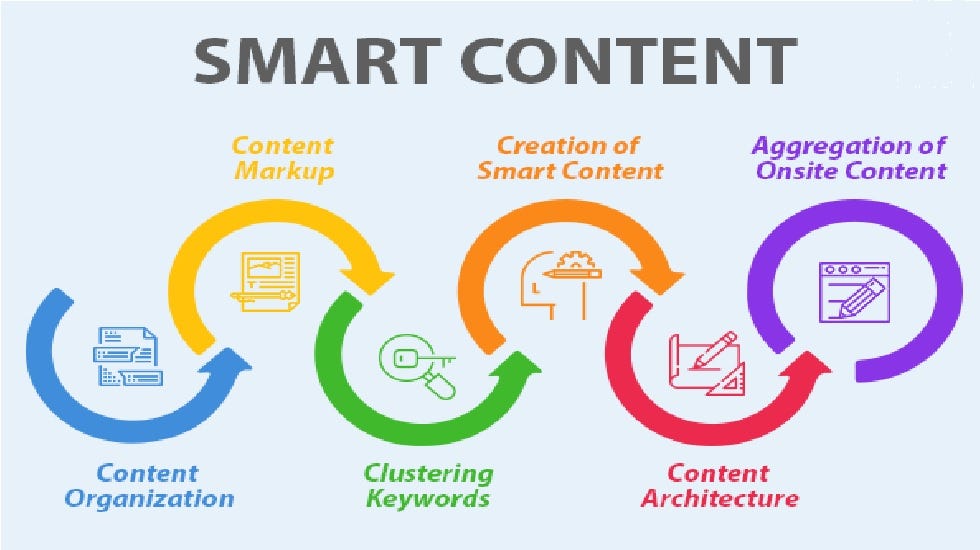
d) AI-Generated Content and Learning Materials
AI can create learning content dynamically—quizzes, flashcards, summaries, and even entire textbooks. By analyzing curriculum requirements and student performance, AI can generate practice materials that align with learning objectives.
For example, platforms like Quizlet and ChatGPT-powered educational apps create adaptive study materials instantly, making studying more engaging and efficient.
e) Real-Time Feedback for Students and Teachers
AI tools can analyze student responses and provide instant feedback, helping learners understand mistakes and improve quickly. For teachers, dashboards display trends, highlight areas where students struggle, and offer actionable insights for lesson planning.
f) Accessibility and Inclusive Education
AI makes education more inclusive for students with disabilities:
Speech-to-text tools assist students with hearing impairments.
Text-to-speech aids visually impaired learners.
Real-time translation and captioning help non-native speakers understand lessons better.
This inclusivity empowers a diverse range of students to succeed in the classroom.
Benefits of AI in Education
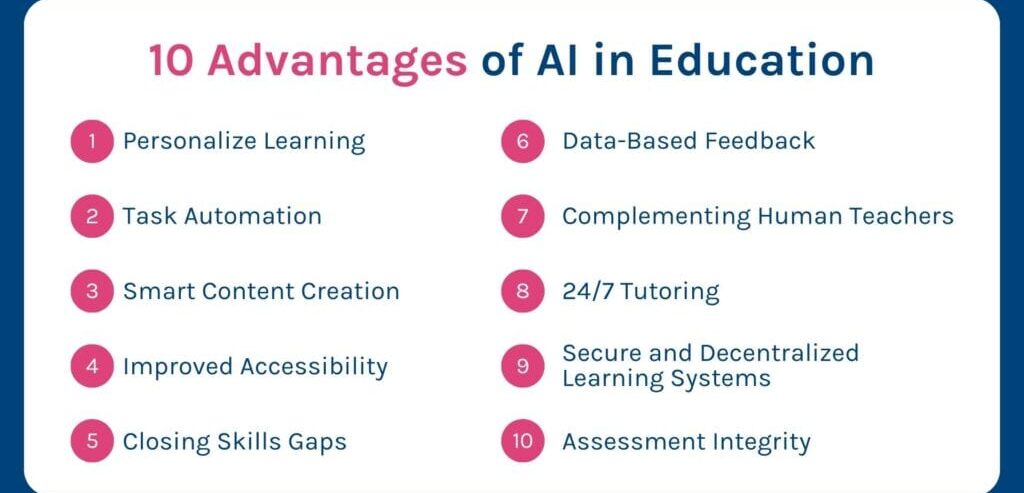
The integration of AI in classrooms brings numerous benefits:
Improved Student Engagement: Interactive AI-driven tools make learning fun and immersive.
Better Learning Outcomes: Personalized and adaptive learning improves retention and test scores.
Efficient Use of Teacher Time: Automation of routine tasks gives teachers more time for high-value teaching.
Scalable Education: AI allows quality learning experiences to reach more students globally, even in underserved areas.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Educators can use real-time analytics to refine teaching strategies and curriculum.
Real-World Examples of AI in Education
Duolingo: AI-powered language learning app offering adaptive lessons.
Squirrel AI: Chinese platform providing personalized tutoring for millions of students.
Gradescope: Automates grading of exams and assignments for educators.
Carnegie Learning: Adaptive math and reading platforms for K–12.
Coursera & Udemy: Using AI to recommend courses tailored to learners’ interests.
These platforms showcase how AI is already a critical part of modern education systems.
Challenges of Implementing AI in Classrooms
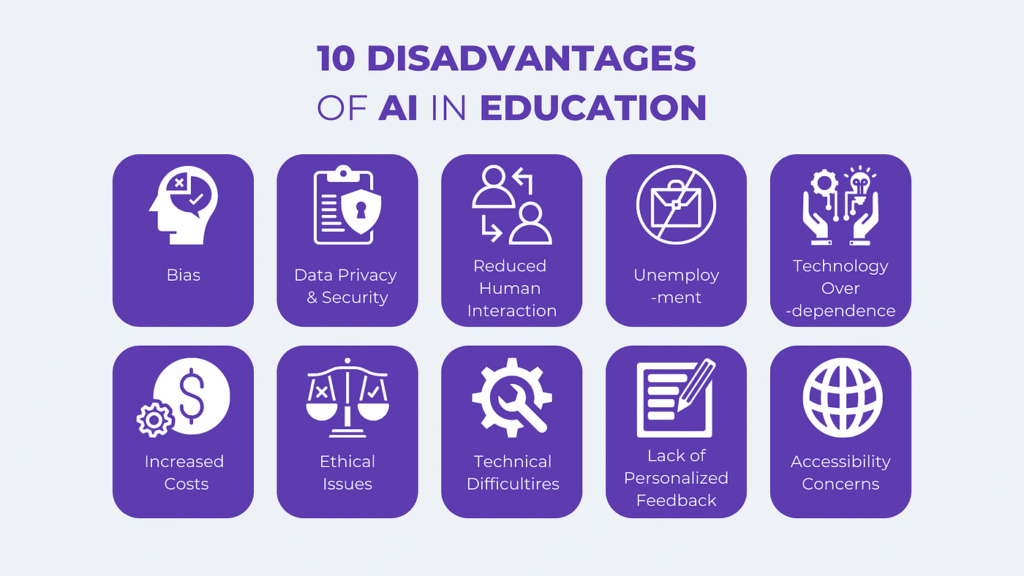
Despite the benefits, AI in education also presents challenges:
Data Privacy Concerns: Collecting and analyzing student data raises privacy and security issues.
Bias in AI Algorithms: If not properly designed, AI systems may reinforce existing biases or inequities.
Teacher Training Needs: Educators need adequate training to integrate AI tools effectively.
Cost and Accessibility: Advanced AI tools may be expensive for schools with limited budgets.
Addressing these challenges requires collaboration between policymakers, educators, and technology providers.
The Future of AI in Education
The future of AI in education looks promising, with several emerging trends:
a) Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR) Classrooms
AI combined with VR and AR will create immersive learning experiences, from exploring the human body in 3D to visiting ancient civilizations virtually.
b) Predictive Analytics for Student Success
AI will increasingly predict student performance and identify at-risk students early, enabling timely interventions.
c) Voice Assistants in Classrooms
AI-driven voice assistants will help students with queries, much like a classroom version of Alexa or Siri, enhancing engagement and reducing the teacher’s workload.
d) Lifelong and Micro-Learning
AI will support continuous learning with bite-sized, adaptive modules tailored to professionals and adult learners.
e) AI-Powered Career Guidance
AI will analyze students’ strengths, interests, and performance to recommend career paths and courses, personalizing guidance beyond traditional counseling.
Ethical Considerations for AI in Education
As AI becomes more integrated into classrooms, ethical issues must be addressed:
Transparency: Students and parents should understand how AI tools work.
Accountability: Schools must ensure responsible use of AI-driven decisions.
Equity: AI should reduce, not widen, the educational gap.
Stakeholders must develop clear policies and frameworks to ensure ethical implementation.
Tips for Educators to Integrate AI in Classrooms
Start Small: Begin with AI tools that automate routine tasks or provide personalized quizzes.
Evaluate Multiple Tools: Choose solutions that align with your curriculum and teaching style.
Focus on Training: Attend workshops or online courses on AI in education.
Encourage Student Feedback: Understand how students perceive and benefit from AI tools.
Maintain Data Privacy: Use platforms that comply with data protection regulations.
Conclusion: AI as a Partner in Learning
Artificial Intelligence in education is not about replacing teachers but enhancing their capabilities. By automating mundane tasks, personalizing learning, and providing actionable insights, AI allows educators to focus on what matters most—nurturing creativity, critical thinking, and human connection.
As technology continues to evolve, the classroom of the future will likely be a hybrid of human expertise and AI-driven innovation. Schools, teachers, parents, and students who embrace AI thoughtfully will lead the way toward a more inclusive, effective, and engaging learning environment.
Related posts:
 How Ancient Indian Education Systems Like Nalanda Shaped Global Learning
How Ancient Indian Education Systems Like Nalanda Shaped Global Learning
 Teaching Kids Cybersecurity in the Digital Age: Essential Tips for Parents
Teaching Kids Cybersecurity in the Digital Age: Essential Tips for Parents
 Unlocking the Secrets of Sleep: How Sleep Physiology Shapes Brain Function
Unlocking the Secrets of Sleep: How Sleep Physiology Shapes Brain Function
 How Street Food Reflects Local Culture: A Culinary Journey Around the World
How Street Food Reflects Local Culture: A Culinary Journey Around the World
 Mind and Body Balance: A Holistic Approach to Health, Happiness, and Success
Mind and Body Balance: A Holistic Approach to Health, Happiness, and Success
 How Stress Affects Digestion – Gut Health & Mental Wellness Connection
How Stress Affects Digestion – Gut Health & Mental Wellness Connection
