Climate change is no longer a distant threat — it’s a global crisis affecting ecosystems, economies, and societies across the planet. Rising temperatures, melting glaciers, deforestation, and extreme weather events are reshaping our world at an alarming rate.
In this urgent fight against climate change, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful ally. With its ability to process vast amounts of data, identify complex patterns, and predict future outcomes, AI is transforming how governments, scientists, and industries respond to environmental challenges.
AI in Climate Prediction and Modeling

Advanced Climate Modeling
Traditional climate models take years of computation and massive datasets to simulate future scenarios. AI algorithms can process these datasets efficiently, learning from satellite imagery, weather sensors, and historical patterns to predict temperature trends, rainfall, and sea-level rise more accurately.
For example, DeepMind’s AI climate model uses machine learning to predict weather patterns in minutes rather than hours, with accuracy comparable to traditional meteorological models.
Early Warning Systems
AI-driven forecasting models are revolutionizing early warning systems for floods, hurricanes, and droughts. By analyzing atmospheric data, AI can detect anomalies and alert communities before disasters strike, potentially saving thousands of lives and billions in damages.
AI in Reducing Carbon Emissions
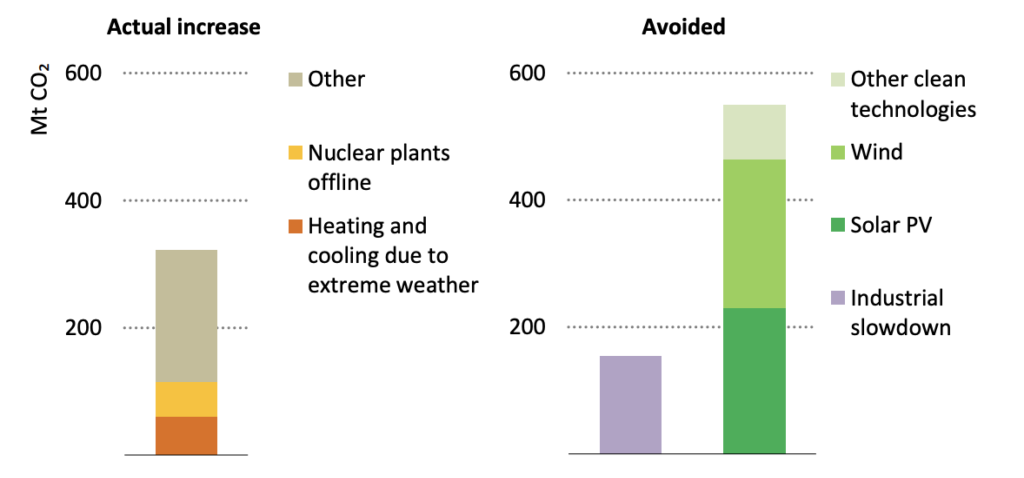
Industrial Efficiency
Industries are among the biggest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. AI helps optimize manufacturing processes, reduce waste, and improve energy consumption.
For example:
Predictive maintenance prevents equipment breakdowns that waste energy.
AI-driven process optimization reduces emissions in steel and cement industries.
IoT and AI together monitor real-time carbon footprints, enabling companies to take corrective actions instantly.
Smarter Transportation
AI is transforming transportation — one of the top sources of carbon emissions. Self-driving algorithms and route optimization systems reduce fuel consumption by identifying the most efficient routes and minimizing idling time.
Ride-sharing apps like Uber and Ola use AI to match drivers and passengers efficiently, reducing the number of vehicles on the road. Meanwhile, electric vehicles (EVs) use AI to optimize battery performance and energy use, promoting a cleaner mode of transport.
AI in Renewable Energy Optimization

Solar and Wind Energy Forecasting
One of the biggest challenges with renewable energy is its intermittent nature — solar panels only work when the sun shines, and wind turbines depend on wind speed.
AI algorithms can predict energy production by analyzing weather data, satellite imagery, and historical output patterns, helping power grids balance supply and demand more efficiently.
Smart Grids
AI-powered smart grids automatically adjust power distribution based on consumption patterns and renewable availability. They can reroute excess energy, store it in batteries, and reduce wastage — making renewable energy more reliable and cost-effective.
Countries like Germany, Japan, and India are already integrating AI into their renewable energy infrastructure to support their 2030 sustainability goals.
AI in Agriculture and Land Use Management
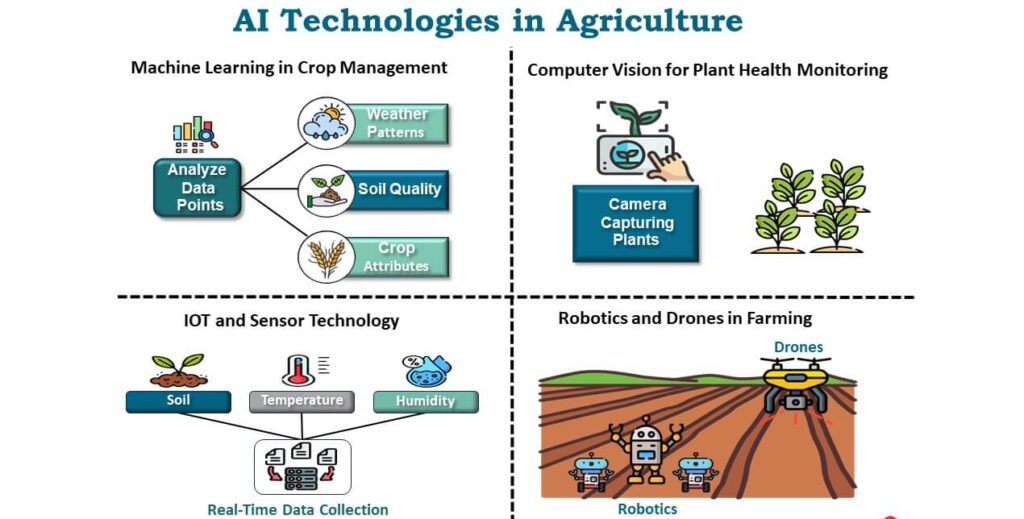
Sustainable Farming with AI
Agriculture contributes nearly 25% of global greenhouse gas emissions, mainly from livestock, fertilizer use, and land degradation. AI is helping farmers make more sustainable choices by providing data-driven insights on:
Soil health and moisture levels
Crop rotation and pest control
Efficient fertilizer and water usage
Precision agriculture, powered by AI drones and sensors, allows farmers to maximize yield while minimizing resource use. This reduces emissions and prevents deforestation caused by land overuse.
Forest Conservation and Deforestation Tracking
AI models trained on satellite imagery can detect illegal logging and deforestation in real time. Tools like Global Forest Watch use machine learning to analyze forest cover changes and alert authorities to take immediate action.
In addition, AI-based reforestation projects are using drones to plant trees in deforested areas — up to 120 trees per minute in some regions!
AI for Sustainable Urban Development
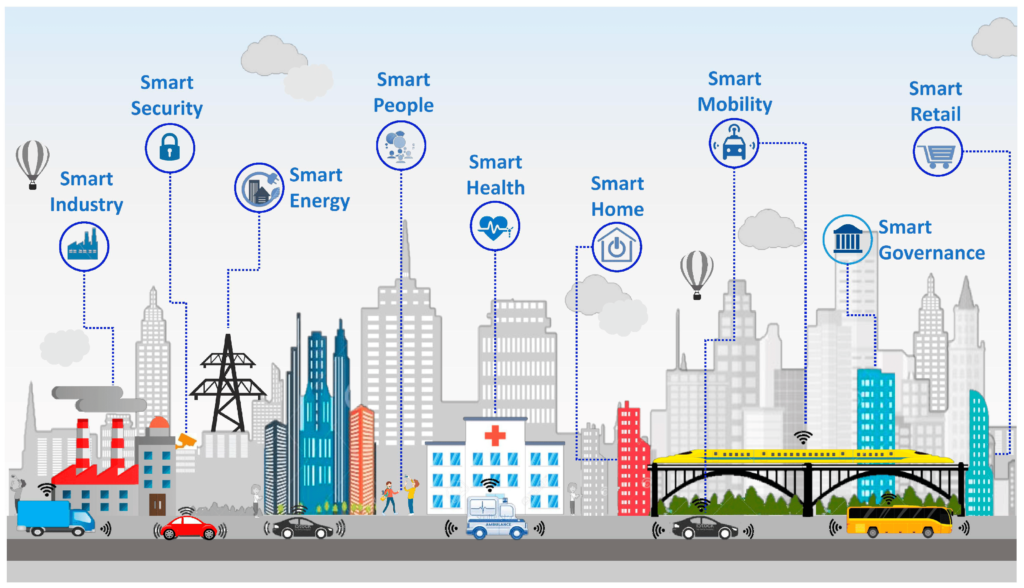
Smart Cities for a Greener Planet
Urban areas account for over 70% of global carbon emissions. AI is helping cities become more sustainable through smart city solutions — integrating IoT sensors, traffic analytics, and energy-efficient systems.
Examples include:
AI-managed traffic lights to reduce congestion and emissions.
Energy-efficient buildings that adjust heating and lighting automatically.
AI-powered waste management systems that optimize recycling routes.
Cities like Singapore, Amsterdam, and Bengaluru are implementing AI-driven smart grids and waste systems to improve sustainability and reduce pollution.
AI in Environmental Monitoring and Conservation
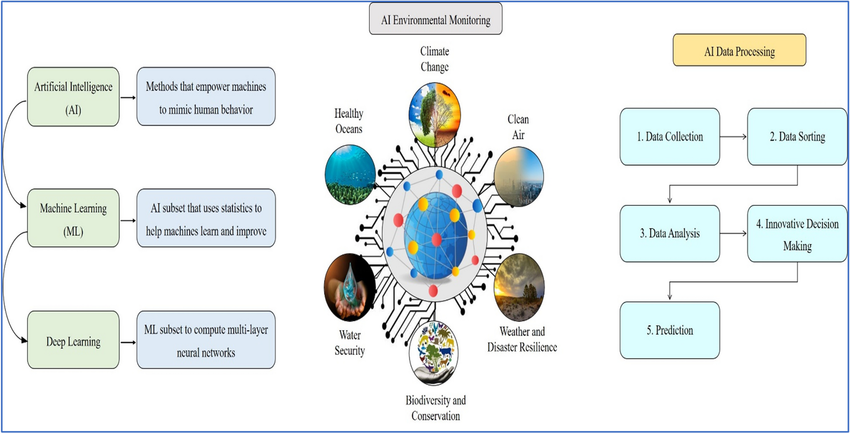
Ocean and Wildlife Monitoring
AI models are being used to track endangered species, monitor coral reefs, and detect ocean pollution. Drones and underwater sensors powered by AI can identify illegal fishing activities, monitor whale populations, and track plastic waste in real time.
For instance, the OceanMind project uses AI to analyze satellite data and ensure that fishing vessels comply with conservation laws — protecting marine biodiversity.
AI in Biodiversity Protection
Machine learning models can identify animal species from camera trap images, allowing conservationists to monitor wildlife populations without disturbing their habitats. AI also predicts the impact of climate change on species migration and survival, helping create better conservation strategies.
AI in Energy Management and Carbon Capture
Smart Energy Storage
AI optimizes the operation of battery energy storage systems (BESS) by predicting demand and controlling charge/discharge cycles. This makes renewable energy storage more efficient, reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
Carbon Capture and Sequestration
AI algorithms are improving the design and operation of carbon capture plants. By analyzing temperature, pressure, and chemical reactions in real time, AI enhances efficiency and reduces operational costs.
Companies like Climeworks and Carbon Clean are using AI to refine their carbon capture processes, bringing us closer to scalable, cost-effective carbon removal.
AI in Climate Finance and Policy
Predictive Climate Risk Assessment
AI helps financial institutions and insurers assess climate-related risks more accurately. By analyzing weather data, satellite imagery, and economic indicators, AI can predict the financial impact of natural disasters and help governments allocate funds more effectively.
Policy Simulation
AI-driven models simulate the outcomes of various climate policies — such as carbon taxes, emission caps, and renewable energy subsidies. This allows policymakers to test scenarios and make data-backed decisions that balance economic growth and sustainability.
Challenges and Ethical Concerns
While AI offers immense potential, it also presents challenges that must be addressed:
Data and Energy Consumption
AI models require massive datasets and computational power, often leading to significant energy consumption. Developing green AI models that run on renewable energy is essential for sustainable innovation.
Data Privacy and Transparency
As AI collects data from satellites, sensors, and personal devices, data privacy and transparency become critical. Ensuring that AI operates ethically and without bias is vital for public trust.
Global Accessibility
Developed countries lead in AI-driven climate research, while developing nations often lack resources. Bridging this gap through open-source AI tools and international cooperation will make climate action truly global.
The Future of AI and Climate Action
By 2030, AI is expected to contribute up to 4% reduction in global greenhouse gas emissions, according to the World Economic Forum. As AI continues to evolve, its applications will expand from forecasting and mitigation to real-time climate intervention and adaptive systems that self-correct environmental impact.
Here are key future trends to watch:
AI-powered climate governance platforms that monitor and enforce emission compliance.
Edge AI devices in remote areas for real-time environmental sensing.
Integration of quantum computing and AI for faster, more accurate climate modeling.
AI-assisted carbon trading systems to optimize carbon offset markets.
In essence, AI is not just a tool — it’s becoming an indispensable partner in building a sustainable and climate-resilient world.
Conclusion: AI for a Sustainable Tomorrow
The role of AI in combating climate change is transformational and indispensable. From predicting climate patterns to optimizing energy use, from protecting forests to designing sustainable cities — AI empowers humanity to make smarter, faster, and more effective climate decisions.
However, technology alone cannot save the planet. The true power of AI lies in how we use it — with responsibility, inclusivity, and a shared vision for sustainability. Governments, businesses, and individuals must collaborate to harness AI for the greater good, ensuring that innovation aligns with environmental ethics.
As we stand at the crossroads of technology and ecology, one thing is clear:
The fight against climate change is not just about saving the Earth — it’s about securing our future. And with AI, that future looks smarter, greener, and more hopeful than ever before.
Related posts:
 Your Life Can Change in Just One Minute – The Ultimate Guide to Success & Motivation!
Your Life Can Change in Just One Minute – The Ultimate Guide to Success & Motivation!
 Breaking the Cycle: Combating Terrorism at Its Ideological Roots
Breaking the Cycle: Combating Terrorism at Its Ideological Roots
 What Was The Role Of Jawaharlal Nehru In Indian Independence Movement?
What Was The Role Of Jawaharlal Nehru In Indian Independence Movement?
 The Role of Chandra Shekhar Azad in Indian Independence
The Role of Chandra Shekhar Azad in Indian Independence
 The Role of Social Media in Promoting or Stopping Violence: A Double-Edged Sword
The Role of Social Media in Promoting or Stopping Violence: A Double-Edged Sword
 The Role of Gut Microbiome in Overall Health: The Hidden Ecosystem Within You
The Role of Gut Microbiome in Overall Health: The Hidden Ecosystem Within You
